Abstract
Background: BTK is a signaling kinase downstream of the B-cell receptor (BCR) and a critical target in CLL. Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) is a highly selective, potent BTK inhibitor developed to minimize off-target activity. Acalabrutinib monotherapy was evaluated in patients (pts) with CLL in the Phase 1/2, open-label ACE-CL-001 study (NCT02029443). Preliminary efficacy and safety data were previously reported (Byrd et al 2016). Acalabrutinib's promising activity in CLL may be due to direct effects on B-CLL cells and indirect effects on the tumor microenvironment. Therefore, we took a comprehensive approach to characterize the drug effects in pts enrolled in the ACE-CL-001 study by measuring BTK occupancy and inhibition of BCR-mediated signaling. We also assessed the impact on B-CLL cells and T cell subsets after drug administration. Because CLL cells have been shown to cause chronic activation of T cells leading to their exhaustion, we monitored changes in PD-1 expression as well as percentage of IFNγ-producing effector T cells. Finally, we investigated changes in plasma cytokine levels.
Methods: PD results reported here were from the relapsed/refractory (R/R) (n=91) and treatment naïve (TN) (n=86) CLL pts who received acalabrutinib at the 100-mg twice daily dose (bid; n=113) and 200-mg once daily dose (qd; n=64) as part of the expansion portion of ACE-CL-001. Blood mononuclear cells and plasma were analyzed at multiple on-treatment timepoints and compared with pre-treatment baseline for the following assays:
BTK occupancy by ELISA method using a drug analogue probe
Total BTK and pBTK after ex vivo BCR-induced signaling by phospho-flow cytometry (FC)
T cell subset counts and PD-1 expression by FC
Percentage of IFNγ-producing T cells in response to phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate/ionomycin stimulation by FC
Levels of 55 cytokines in plasma via Luminex
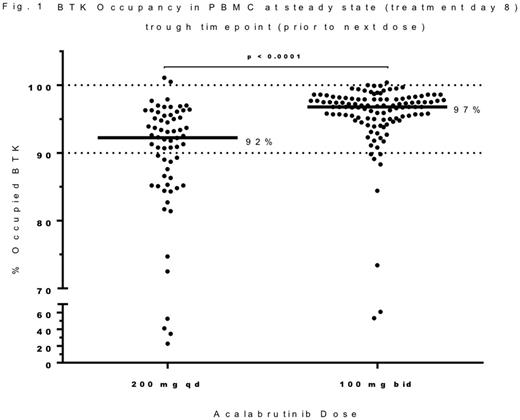
Results: TN and R/R pts treated with acalabrutinib 100 mg bid had a median BTK occupancy of 97% at trough (12h post-dose) at steady state (treatment day 8) of which 95% of pts had BTK occupancy ≥90% (Figure 1). In comparison, pts treated with 200 mg qd had lower median BTK occupancy (92%; p<0.01) at trough (24h post-dose) with only 66% of pts ≥90%. Interpatient variability (%CV) was 6.5% and 16.4% for the bid and qd doses, respectively. Inhibition of pBTK was observed with both treatment regimens (p<0.0001 vs pre-dose values). The levels of pS6 and pAKT(S473) varied among pts over time, and were either not inhibited or only partially inhibited, indicating that BTK inhibition did not block all BCR-induced signaling. A decrease in total BTK was observed in B-CLL cells (p<0.0001 vs pre-dose values), in line with inhibition of an auto-regulatory positive feedback loop of activated BTK.
After 9 months of treatment, 65/91 (71%) of pts had absolute T cell counts within normal limits, including 25/35 (71%) who started treatment having T cells above the normal limit. A decrease in the percentage of PD-1+CD4+ T cells was observed after 6 months on treatment (p<0.0001), which may reflect a decrease in T cell exhaustion. In line with this, there was an increase in the percent of CD8+ T cells capable of producing IFNγ in R/R pts (n=32) after 6 months of treatment (p=0.007). Together, these data suggest a reversal of a T cell exhausted state. Finally, plasma levels of 18 cytokines decreased (p<0.001 vs predose) after 28 days of acalabrutinib treatment, notably CCL3, CCL4, CXCL13, IP-10, IL-10 and TNFα, providing further evidence of tumor microenvironment modulation (Herishanu et al 2011; Niemann et al 2016).
Conclusions: As BTK synthesis rates may vary across pts, a dosing regimen that maintains high target coverage over each dose interval, with minimal interpatient variability, may be beneficial. This study showed the 100-mg bid dosing regimen led to near complete BTK occupancy with lower interpatient variability compared with 200 mg qd. Acalabrutinib treatment resulted in an expected decrease in pBTK and reduced total BTK levels in B-CLL cells. In addition to the direct impact on the leukemia cells, acalabrutinib treatment had indirect effects on the tumor microenvironment that may also contribute to an antitumor response. Together, these data provide a comprehensive assessment of acalabrutinib's pharmacodynamic effects in pts with CLL. Acalabrutinib 100 mg bid is currently being evaluated in three phase 3 studies in pts with CLL (NCT02477696, NCT02970318 and NCT02475681).
Covey: Astra-Zeneca: Equity Ownership; Acerta: Employment, Equity Ownership. Gulranjani: Acerta: Employment, Equity Ownership; Astra-Zeneca: Equity Ownership. Cheung: Acerta: Employment, Equity Ownership; Astra-Zeneca: Equity Ownership. Bibikova: Acerta Pharma: Employment; Acerta Pharma: Equity Ownership; Astra-Zeneca: Equity Ownership. Clevenger: Acerta Pharma: Employment; Astra Zeneca: Equity Ownership. Krantz: Acerta Pharma: Employment. Pan: Acerta Pharma: Employment. De Jong: Acerta Pharma: Employment. Mittag: Acerta Pharma: Employment. Izumi: Acerta Pharma: Employment, Equity Ownership. Byrd: Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; The Ohio State University: Patents & Royalties: OSU-2S. Wierda: Acerta: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Emergent: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genzyme: Consultancy, Honoraria; GSK/Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center: Employment; Juno: Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria; Kite: Research Funding. O'Brien: Astellas: Consultancy; ProNAI: Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Sunesis: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy; Regeneron: Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Vaniam Group LLC: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy; Acerta: Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; CLL Global Research Foundation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aptose Biosciences, Inc.: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Alexion: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy; Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Consultancy, Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding. Furman: Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Sunesis: Consultancy; Verastim: Consultancy. Kaptein: Acerta Pharma: Consultancy; Acerta Pharma: Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal